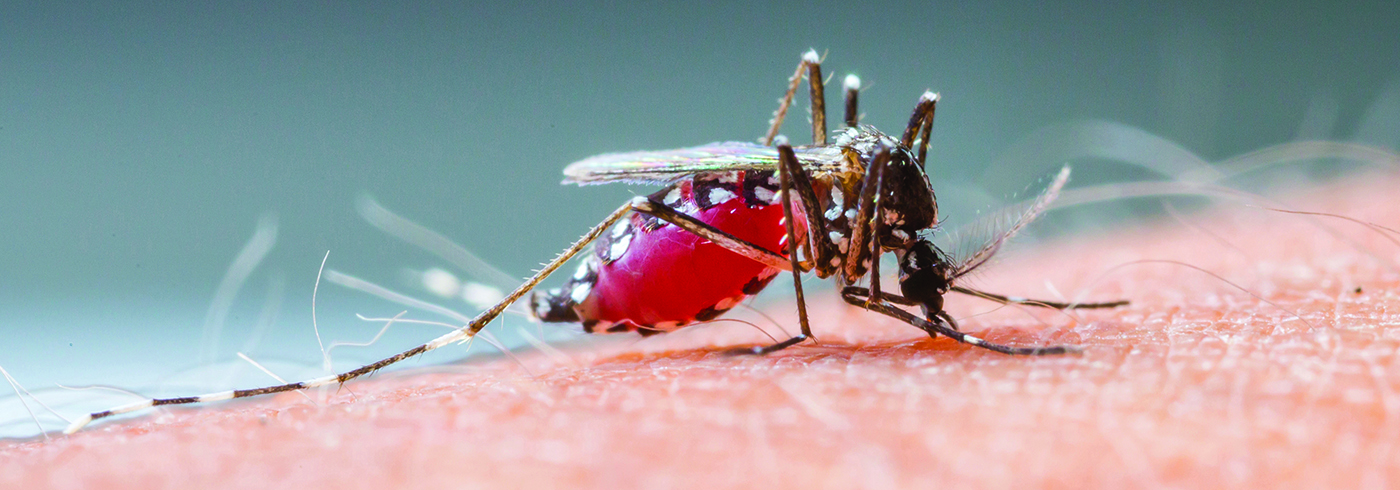
West Nile Virus
West Nile virus (WNV) is mostly a disease that affects birds. However, it can be spread to humans by mosquitoes that feed on both birds and humans. Not all mosquitoes carry the WNV.
WNV surveillance activities
2025 weekly adult mosquito surveillance results in Durham Region
West Nile Virus in Durham Region infographic
Protect yourself against West Nile virus
| Signs and symptoms |
Mild symptoms include:
Severe symptoms include:
|
| Diagnosis, testing and treatment |
DiagnosisA diagnosis of WNV is based on symptoms and a known exposure to mosquitoes. TestingBlood or spinal fluid testing can be used to confirm WNV infection. TreatmentThere is no vaccine or specific treatment for WNV infection. You can use over-the-counter pain relievers to reduce fever and relieve some symptoms. In severe cases, patients may need to go to the hospital to get treatment. This could include:
|
| Protect yourself |
|
The most effective way to avoid WNV infection is to prevent mosquito bites. Be aware of the West Nile virus activity in your area. Take action to protect yourself and your family. You can reduce your risk of being infected with WNV by using insect repellent, wearing protective clothing to prevent mosquito bites, and eliminating stagnant water on your property. |
| How is it spread? |
|
A bite of an infected mosquito spreads WNV.
|
| Role of the Health Department |
The Durham Region Health Department conducts surveillance and control activities for WNV. These include:
|
| Additional information |
Online services
Durham Region Health Department investigates reports of stagnant water on publicly owned property and facilitates the application of larviciding to backyard catch basins to reduce the breeding of mosquitoes for the prevention of the spread of West Nile virus.
The Health Department’s West Nile virus surveillance season has concluded for 2025. This program runs from May to September each year.
Contact Us